|
Title |
Triarylboron-based TADF emitters with perfluoro substituents: high-efficiency OLEDs with a power efficiency over 100 lm W-1 |
|
Author list |
Kumar, Ajay; Lee, Woochan; Lee, Taehwan; Jung, Jaehoon; Yoo, Seunghyup; Lee, Min Hyung |
|
Publication date |
2020/03 |
|
Citation information |
Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 8, 4253 (2020). |
|
DOI |
10.1039/C9TC06204A |
|
Graphical Abstract |
|
|
Abstract |
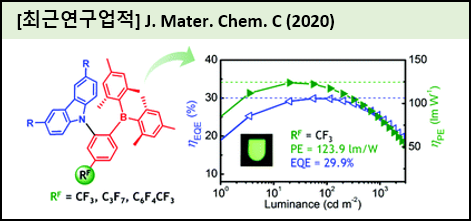
We report boron-based thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) emitters that can lead to high-efficiency organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) with high power efficiency and low driving voltage. ortho-Carbazole-appended triarylboron compounds (2-7), in which perfluoroalkyl (CF3 and C3F7) or perfluoroaryl (4-CF3C6F4) groups are attached as secondary acceptors, are prepared and characterized. The compounds exhibit a light greenish to yellow emission in toluene with high photoluminescence quantum yields up to 100%. The twisted donor (D)-acceptor (A) structure, as evidenced by both the X-ray crystal structures and theoretically optimized structures, leads to a small energy splitting (ΔEST < 0.1 eV) between the excited singlet and triplet states, giving rise to strong TADF. High-efficiency TADF-OLEDs are realized with the CF3- and 4-CF3C6F4-substituted compounds as emitters. The optimized OLEDs based on the CF3-substituted emitter (5) show a high external quantum efficiency of 29.9% with a low turn-on voltage of 2.35 V. In particular, the devices achieve an ultrahigh power efficiency (PE) of 123.9 lm W?ithout any light-outcoupling enhancement, which is among the best PE values for the reported TADF-OLEDs. The devices also maintain a high PE at the practical brightness, such as 100 cd m?2(118.7 lm W?1) and 1000 cd m?2 (82.3 lm W?1). |
|

