|
Abstract
(superscript and subscript cannot be allowed.) |
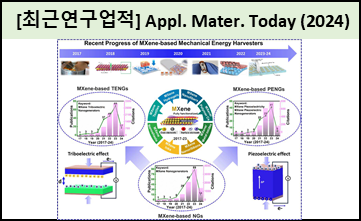
Recently developed nanogenerators (NGs) represent a promising technology capable of converting mechanical energy from environmental sources into electrical energy using piezoelectricity and triboelectricity. Transition metal carbides/nitrides (MXene) have emerged as novel energy-harvesting materials for both piezoelectric NGs (PENGs) and triboelectric NGs (TENGs). Nevertheless, MXene-based NGs face challenges related to poor output performance and environmental stability- aspects not thoroughly explored in previous reviews. Therefore, there is a compelling need to delve into fundamental issues and critical material aspects influencing the performances of MXene-based NGs. This review predominantly concentrates on both positive and negative sides of MXene, emphasizing strategies to enhance the overall performance of NGs. The state-of-the-art MXene-based PENGs and TENGs are discussed, and fundamental issues and major drawbacks responsible for poor performance are reviewed. Furthermore, future perspectives and effective synthetic approaches to improving the MXene surface for its effective application in NGs are examined. The aim is to appraise the rational structures of MXene for piezoelectric and triboelectric energy harvesting and to explore future perspectives and remaining challenges in the field. |