|
Title |
Control of side reactions using LiNbO3 mixed/doped solid electrolyte for enhanced sulfide-based all-solid-state batteries |
|
Author list |
Ji-Un Cho, Rajesh Rajagopal, Da Hye Yoon, Yong Joon Park*, Kwang-SunRyu* |
|
Publication date |
2023/01 |
|
Citation information |
Chemical Engineering Journal, Volume 452, Part 1, 15 January 2023, 138955 |
|
Abbreviation of Journal Name |
Chemical Engineering Journal |
|
DOI |
10.1016/j.cej.2022.138955 |
|
Graphical Abstract
(Do not change the size of box, and also do not remove the citation information.) |
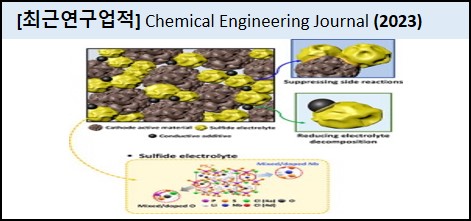
|
|
Abstract
(superscript and subscript cannot be allowed.) |
LiNbO3 coating. Partial doping of LiNbO3 was confirmed by laser Raman spectroscopy and field-emission scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) analysis. An optimum LiNbO3 mixed/doped electrolyte (4 mol.% of electrolyte) showed enhanced ionic conductivity than that of Li6PS5Cl solid electrolyte without LiNbO3. Moreover, the interfacial reaction at the cathode/electrolyte interface and the sulfide electrolyte decomposition were decreased owing to the LiNbO3 mixing/doping effect. The suppression of ion exchange between the cathode and electrolyte was also confirmed by the scanning transmission electron microscopy - energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (STEM-EDS) line profile. These results contributed to the increased discharge capacity and improved rate capability of the cell using 96LPSCl-4LNO (4 mol.% LiNbO3 mixing/doping), compared to those of the cell using pristine Li6PS5Cl. |