|
Title |
Enzyme-Mediated Kinetic Control of Fe3+-Tannic Acid Complexation for Interface Engineering |
|
Author list |
Lee, Hojae; Nguyen, Duc Tai; Han, Sang Yeong; Hong, Yeo Jin; Yun, Gyeongwon; Kim, Beom Jin; Choi, Insung S. |
|
Publication date |
2021/11 |
|
Citation information |
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 13, 52385-52394 (2021)
|
|
DOI |
10.1021/acsami.1c15503 |
|
Graphical Abstract |
|
|
Abstract |
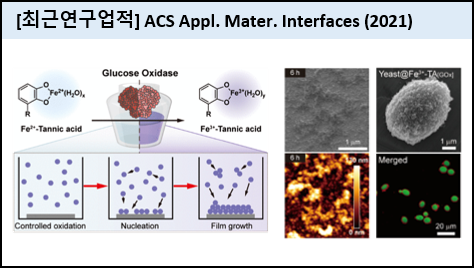
Supramolecular self-assembly of Fe3+ and tannic acid (TA) has received great attention in the fields of materials science and interface engineering because of its exceptional surface coating properties. Although advances in coating strategies often suggest that kinetics in the generation of interface-active Fe3+-TA species is deeply involved in the film formation, there is no acceptable elucidation for the coating process. In this work, we developed the enzyme-mediated kinetic control of Fe2+ oxidation to Fe3+ in a Fe2+-TA complex in the iron-gall-ink-revisited coating method. Specifically, hydrogen peroxide, produced in the glucose oxidase (GOx)-catalyzed reaction of d-glucose, accelerated Fe2+ oxidation, and the optimized kinetics profoundly facilitated the film formation to be about 9 times thicker. We also proposed a perspective considering the coating process as nucleation and growth. From this viewpoint, the kinetics in the generation of interface-active Fe3+-TA species should be optimized because it determines whether the interface-active species forms a film on the substrate (i.e., heterogeneous nucleation and film growth) or flocculates in solution (i.e., homogeneous nucleation and particle growth). Moreover, GOx was concomitantly embedded into the Fe3+-TA films with sustained catalytic activities, and the GOx-mediated coating system was delightfully adapted to catalytic single-cell nanoencapsulation. |
|