|
Title |
Role of chemical interface damping for tuning chemical interface enhancement in resonance surface-enhanced Raman scattering of plasmonic gold nanorods |
|
Author list |
Seo, Min Jung; Kim, Geun Wan; Tsalu, Philippe Vuka; Moon, Seong Woo; Ha, Ji Won |
|
Publication date |
2020/02 |
|
Citation information |
Nanoscale Horizons, 5, 345 (2020) |
|
DOI |
10.1039/C9NH00524B |
|
Graphical Abstract |
|
|
Abstract |
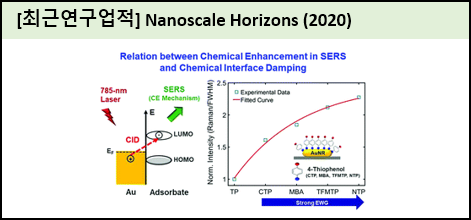
In surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), two complementary SERS enhancement mechanisms are known: electromagnetic enhancement (EME) and chemical enhancement (CE). Herein, we demonstrated, by exciting SERS with a well-suited laser wavelength near the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) of gold nanorods (AuNRs), that the CE contribution to the SERS signal can be selectively tuned and quantified through its correlation with chemical interface damping (CID), one of the LSPR decay processes in AuNRs. We further elucidated probe electrophilicity of a series of para-substituted aromatic thiophenols through a strong gold-sulfur interaction that plays an important role in hot-electron charge transfer from AuNRs to adsorbates, effectively increasing the CE. Therefore, our findings reveal that strong CID must significantly increase the CE for SERS to allow tuning of the CE under resonant conditions. |
|

